Welcome to the Digital Operations Risk & Technology Assessment
The fourth industrial revolution - enabled by the emerging technologies of today and characterized by the increasing digitization and interconnection of products, value chains and business models - has arrived in every sector and offers attractive opportunities. It not only comprises the digitization of horizontal and vertical value chains but will also revolutionize company product and service portfolios and lead to the implementation of new, often disruptive business models.
When starting the journey of adopting these revolutionary technologies, or during this process, it is of great value to think of the steps you have taken to stay in control of the technology and the processes that are built around it. The Risk & Technology assessment will help you do so. It is meant to provide you with an understanding of your company's position regarding the risks that come with the use of emerging technologies. By measuring your actual against your target maturity along five dimensions, we will identify the needed actions to become a digital trust champion, which is vital for your digital journey and sends a strong signal to your clients, suppliers and other important stakeholders. In order to take your understanding to the next level, register for the benchmark after having completed the assessment to gain valuable insights on how you are positioned against competitors in your industry.

These eight technologies are essential and reshaping today
Technology is evolving at breakneck speed and is already defining what’s next — for your company, competitors, and industry. These Essential 8 technologies: Artificial intelligence, augmented reality, blockchain, drones, IoT, robotics, virtual reality, and 3-D printing matter most for business today.
The new tech future is here
Technology is evolving at breakneck speed and is already defining what’s next — for your company, competitors, and industry. Business leaders understand this: 76% of CEOs in our annual survey are worried about the speed of tech change. And 64% acknowledge that changes in the technology used to run their businesses will be disruptive over the next five years. Emerging technology should be a key part of every company’s corporate strategy. So why are so many hesitant to take action?
To help companies focus their emerging tech efforts, we analyzed the business impact and commercial viability of more than 250 emerging technologies to zero in on the “Essential Eight.” These are the core technologies that matter most for business, across every industry, over the next three to five years. The Essential Eight are the technology building blocks that we believe every organization must consider. While each company’s strategy for how to best exploit — and combine — them will vary, these technologies will have a profound global impact on business, employees, and customers.
Explore the Essential Eight
- Artificial intelligence
- Augmented reality
- Blockchain
- Drones
- Internet of Things
- Robotics (RPA)
- Virtual reality
- 3-D printing
Artificial intelligence
Robots are machines with enhanced sensing, control, and intelligence used to automate, augment, or assist human activities. The robot market, which has grown for industrial applications, is poised for growth in a broad range of services applications. These applications are transforming manufacturing and non-manufacturing operations with new capabilities that address the challenges of working in changing, uncertain, and uncontrolled environments, such as alongside humans without being a danger to them.
Augmented reality
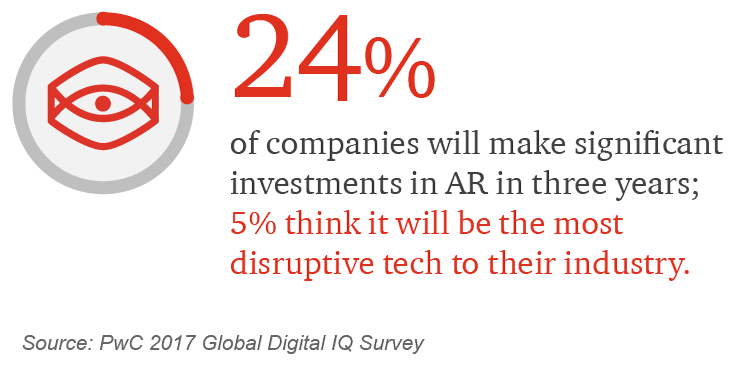
Augmented reality (AR) is a visual or audio “overlay” on the physical world that uses contextualized digital information to augment the user’s real-world view. AR-enabled smart glasses help warehouse workers fulfill orders with precision, airline manufacturers assemble planes, and electrical workers make repairs. We’re currently seeing mainstream gaming examples of AR that span age demographics. The power of bringing information to the point of action in a seamless, unobtrusive manner is undeniable. This blending of the physical and virtual worlds is cracking open a new realm for businesses across the board to explore.
Blockchain
A blockchain is a distributed digital database or, more broadly, a digital ledger that uses software algorithms to record and confirm transactions with reliability and anonymity. The record of events is shared between many parties and information once entered cannot be altered. Blockchain has the potential to usher in an era of autonomous digital commerce.

Drones
Depending on their design, drones vary greatly in their capacity. Some drones need wide spaces to take off, while quadcopters can squeeze into a column of space. Some drones are water based; others can operate and navigate autonomously (via remote control) or fully autonomously (via onboard computers). Companies are using drones for wide-ranging reasons, including surveillance, survey, sport, cinematography, and delivery.

Internet of Things
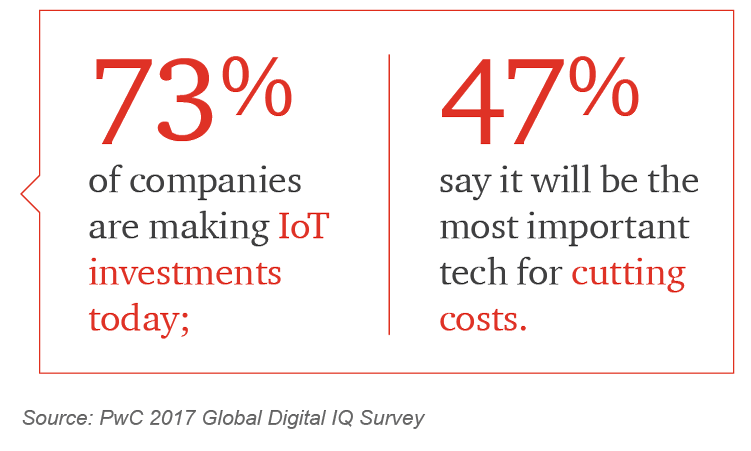
The Internet of things (IoT) is a network of physical objects — devices, vehicles, appliances — embedded with sensors, software, network connectivity, and computing capability enabling them to collect, exchange, and act on data, usually without human intervention. The industrial IoT (IIoT) refers to its use in the manufacturing and industrial sectors, aka Industry 4.0. IIoT augments people, places, processes, and products with sensors to capture and analyze information across a value chain, advancing the goals of the organization.
Robotics (RPA)
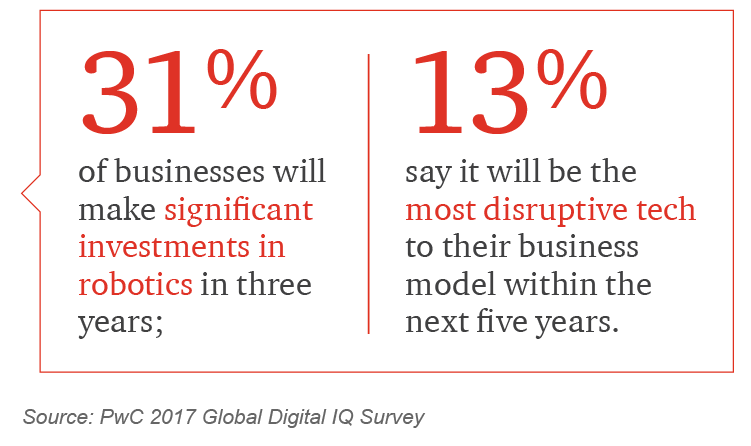
Robots are machines with enhanced sensing, control, and intelligence used to automate, augment, or assist human activities. The robot market, which has grown for industrial applications, is poised for growth in a broad range of services applications. These applications are transforming manufacturing and non-manufacturing operations with new capabilities that address the challenges of working in changing, uncertain, and uncontrolled environments, such as alongside humans without being a danger to them. Where Robotics is about physical robots, Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is about software that performs manual, time-consuming and rules-based office tasks more efficiently by reducing cycle time and at lower costs than other automation solutions.
Virtual reality
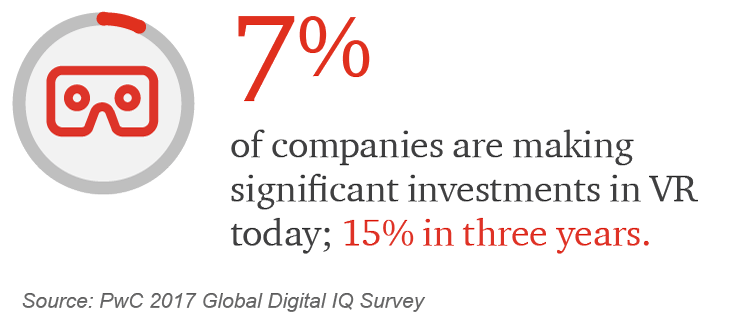
Virtual reality (VR) abolishes logistical limitations and makes anything possible. In a computer-generated simulation of a three-dimensional image or environment, viewers can use special equipment to interact with the simulation in realistic ways. The gaming and entertainment industries are obvious proving grounds for VR. However, VR has the potential to transform many other industries as well, especially in the realm of experiential training where workers can be put into hazardous, difficult, or cost-prohibitive situations without the intense risks associated with these activities in the real world.
3-D printing
3-D printing creates three-dimensional objects based on digital models by layering or “printing” successive layers of materials. 3-D printing relies on innovative “inks,” including plastic, metal, and, more recently, glass and wood. 3-D printing has the potential to turn every large enterprise, small business and living room into a factory.
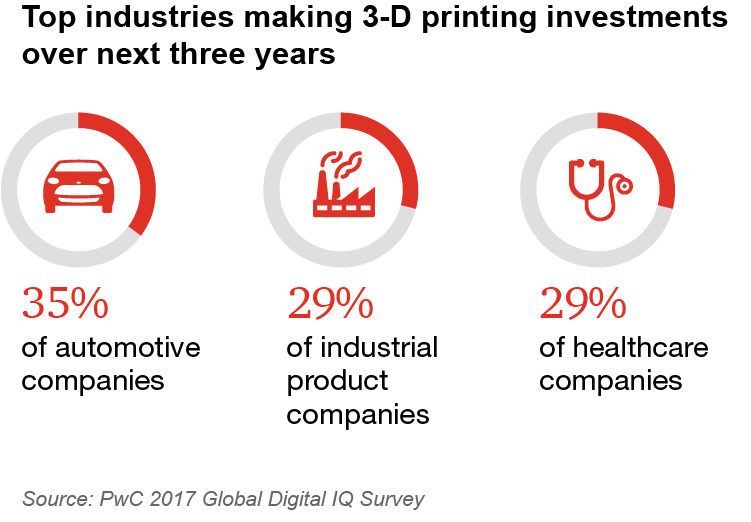
What your peers think about the Risks and Technology challenges of Digital Operation
For the Global Digital Operations Study we, together with Strategy&, conducted interviews with more than 1,100 senior executives from industrial products companies in 26 countries over the world. This study provides insights in how to manage the transition in becoming a digital champion.
In addition, we surveyed more than 2,000 executives and board members in risk management, compliance and internal audit, to explore the things that differentiate risk functions in a digital transformation. We identified that organisations with more-digitally-fit risk functions are seeing greater benefits from their digital initiatives.
|
By plugging into the organization’s digital strategy, risk functions can help establish digital governance so that appropriate guide rails transcend initiatives scattered across the organisation |
|
Identifying the knowledge and capabilities a risk function needs to have in place is a prerequisite for building digital fitness. |
|
Organisations with more-digitally-fit risk functions are seeing greater benefits from their digital initiatives |
|
While many technology risks are not new, the stakes are now much higher as digital rollouts heighten the risks beyond the technology itself. |
|
The key to success for digital transformation is a holistic approach in connecting essential technologies across the organization and with strategic partners instead of isolated implementations. |
"Why do you put brakes on cars? Most people would say, 'Well, you have to be able to stop.' No, it's so you can have the car go faster and still be in control.”
What We Think About Digital Operations
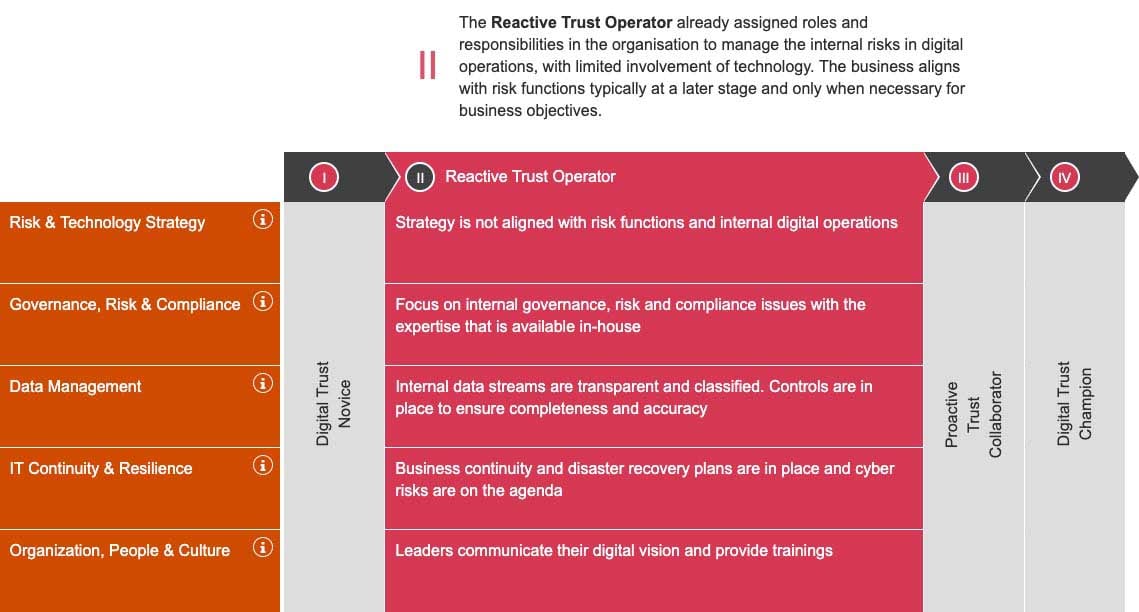
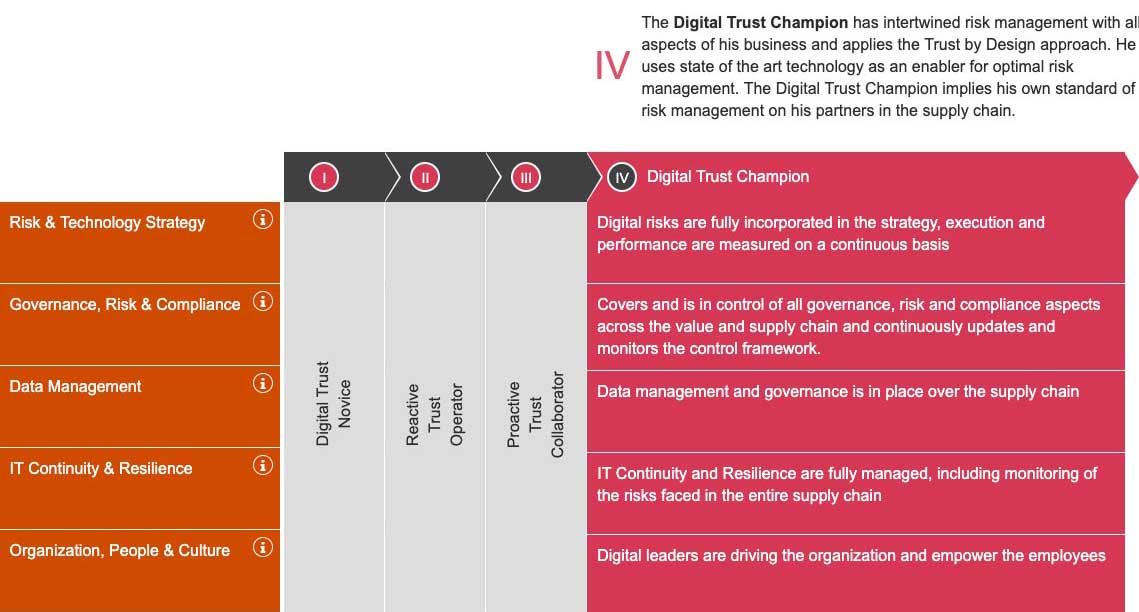
To share our vision on how to manage the risks of emerging technologies we created a maturity model which includes the most relevant functional dimensions as well as the maturity stages a company can be in. We use it to help companies understand where they currently are on their digital trust journey and which next steps are sensible in respect to their current situation and the industry they are operating in. The maturity model serves as a basis for the Risk & Technology Assessment, so your current maturity level will be shown as part of the result.


Contact us